How Do Monstera Plants Reproduce: A Comprehensive Guide
Monstera plants reproduce through both seeds and cuttings. They can also reproduce through air layering, which is a method of creating a new plant while still attached to the parent plant.
Monstera plants, known for their large, distinctive leaves, are popular houseplants. Understanding how they reproduce can help you propagate them at home. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or a novice, knowing the basics of plant reproduction is key. Monstera plants offer multiple ways to propagate, making them accessible for everyone.
From using seeds to taking cuttings, each method has its own steps and benefits. By learning these methods, you can expand your plant collection easily and enjoy the beauty of Monstera plants in your home.
Introduction To Monstera Plants
Monstera plants are well-loved for their unique, perforated leaves and lush, tropical appearance. These plants can add a touch of the jungle to any home or garden. Understanding how they reproduce can help you grow more of these beautiful plants.
Brief History
The Monstera plant, also known as the Swiss Cheese Plant, originates from the tropical forests of Central and South America. The name “Monstera” comes from the Latin word for “monstrous” due to its unusually large leaves with natural holes.
In the wild, Monstera plants climb up trees, reaching for sunlight. They can grow very large, sometimes up to 70 feet. Inside homes, they are often grown as houseplants, bringing a bit of the tropics indoors.
Popular Varieties
There are several popular varieties of Monstera plants, each with unique characteristics.
| Variety | Description |
|---|---|
| Monstera Deliciosa | Known for its large, heart-shaped leaves with deep splits and holes. |
| Monstera Adansonii | Features smaller leaves with numerous oval-shaped holes. |
| Monstera Obliqua | Rare variety with delicate, almost lace-like leaves. |
Other varieties include Monstera Borsigiana, a smaller version of Monstera Deliciosa, and Monstera Siltepecana, known for its silver-blue leaves.
These varieties are all part of the Araceae family and share similar care needs.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SPR-how-to-propagate-monstera-04-bd6b8ebc682f4a03baa6ece4fd8a75e9.jpg)
Natural Habitat
The natural habitat of Monstera plants is fascinating. They thrive in specific regions and climates. Understanding their natural surroundings helps in growing them indoors.
Geographic Distribution
Monstera plants are native to tropical areas. They are found in Central and South America. Countries like Mexico, Panama, and Colombia host these plants. They also grow in parts of the Caribbean.
Climate Preferences
Monstera plants love warm, humid climates. They flourish in rainforests where humidity is high. The temperature should be between 65°F to 85°F. They need indirect sunlight and plenty of moisture. These conditions mimic their natural habitat.
Reproduction Methods
Monstera plants are popular for their unique leaves and easy care. Understanding their reproduction methods helps in growing more plants at home. Monstera plants can reproduce in two primary ways: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. Each method has its own process and benefits.
Sexual Reproduction
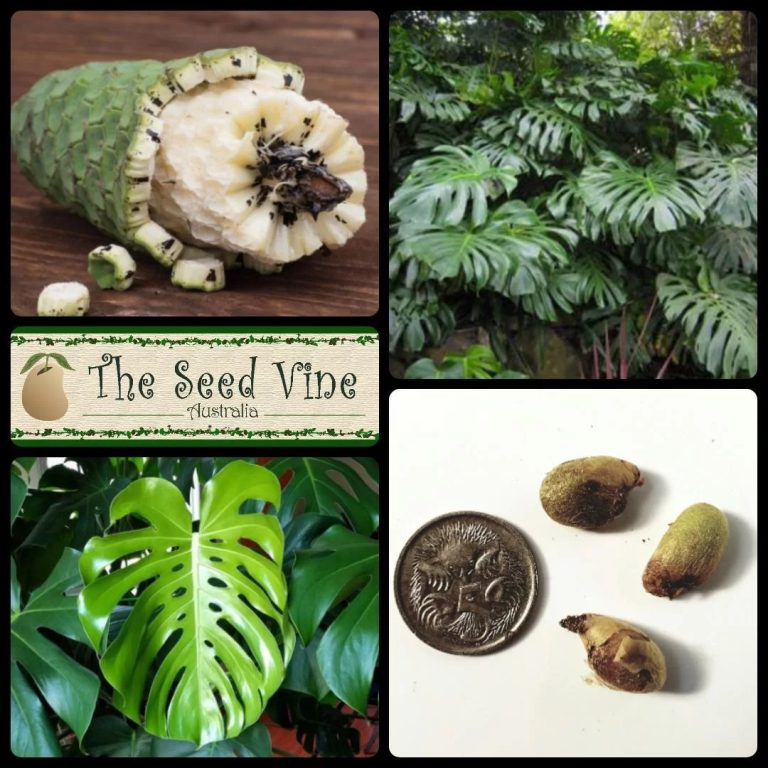
Sexual reproduction in Monstera plants involves seeds. These seeds come from flowers. The flowers must be pollinated to produce seeds. Pollination can occur naturally or through human intervention.
Pollinators like insects help transfer pollen. In some cases, gardeners use tools to pollinate manually. After pollination, seeds develop within the flower. These seeds grow into new Monstera plants when planted.
Asexual Reproduction
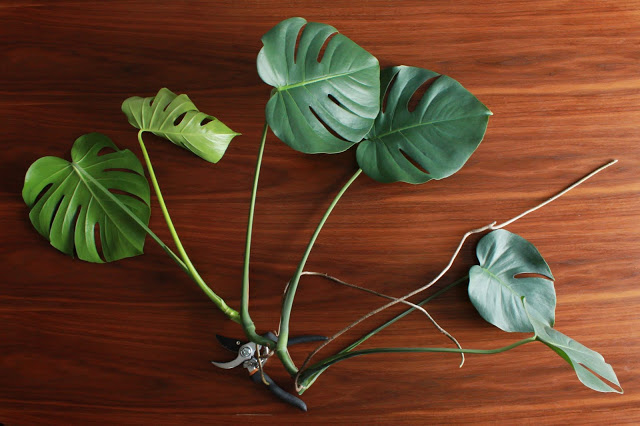
Asexual reproduction is common for Monstera plants. It involves creating new plants from parts of the original plant. The most popular method is stem cuttings. Take a healthy stem with a few leaves. Place the stem in water or soil. Roots will develop from the stem, forming a new plant.
Another method is air layering. Choose a healthy stem and make a small cut. Wrap the cut area with moist sphagnum moss. Cover it with plastic wrap to keep moisture in. Roots will grow from the cut area. Once roots are visible, cut the stem below the roots and plant it in soil.
Both methods are effective and easy for home gardeners. Asexual reproduction ensures the new plant will be identical to the parent plant.
Pollination Process
Monstera plants reproduce through a fascinating pollination process. This process involves the transfer of pollen from one flower to another. This crucial step enables the plant to produce seeds. Two primary methods of pollination occur in Monstera plants: insect pollination and self-pollination.
Role Of Insects
Insects play a vital role in the pollination of Monstera plants. They visit the flowers to collect nectar. As they move from flower to flower, they carry pollen with them. This pollen transfer helps fertilize the flowers. Bees and beetles are common pollinators for Monstera plants.
Self-pollination
Monstera plants can also self-pollinate. This happens when a flower transfers its own pollen to its stigma. Self-pollination ensures reproduction even if no insects are around. This method is an excellent backup for the plant. It increases the chances of successful seed production.
Seed Germination
Seed germination is a key part of Monstera plant reproduction. Learning how to germinate Monstera seeds can help you grow these stunning plants at home. This section will cover seed collection and germination conditions for Monstera plants.
Seed Collection
Monstera plants produce seeds inside their fruit. Wait until the fruit is fully ripe. The fruit will start to fall apart. Carefully collect the seeds from the fruit. Ensure the seeds are clean and dry before planting.
Germination Conditions
Monstera seeds need specific conditions to germinate. Follow these steps to create the ideal environment:
- Temperature: Maintain a warm environment, around 70-85°F (21-29°C).
- Humidity: Keep the humidity high, around 70-80%.
- Light: Provide bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight.
- Soil: Use a well-draining soil mix. A mix of peat moss and perlite works well.
- Water: Keep the soil moist but not soggy. Overwatering can cause rot.
Using a humidity dome can help maintain high humidity levels. Place the seeds on the soil surface and lightly cover them. Keep the soil temperature consistent for better results.
Patience is key, as Monstera seeds can take several weeks to germinate. Check the seeds regularly and keep the conditions stable.
Propagation Techniques
Monstera plants, with their unique, perforated leaves, are a favorite among plant enthusiasts. These tropical beauties can be propagated through various techniques, allowing you to grow new plants from a single parent. Let’s explore the most effective methods to propagate your Monstera plants.
Stem Cuttings
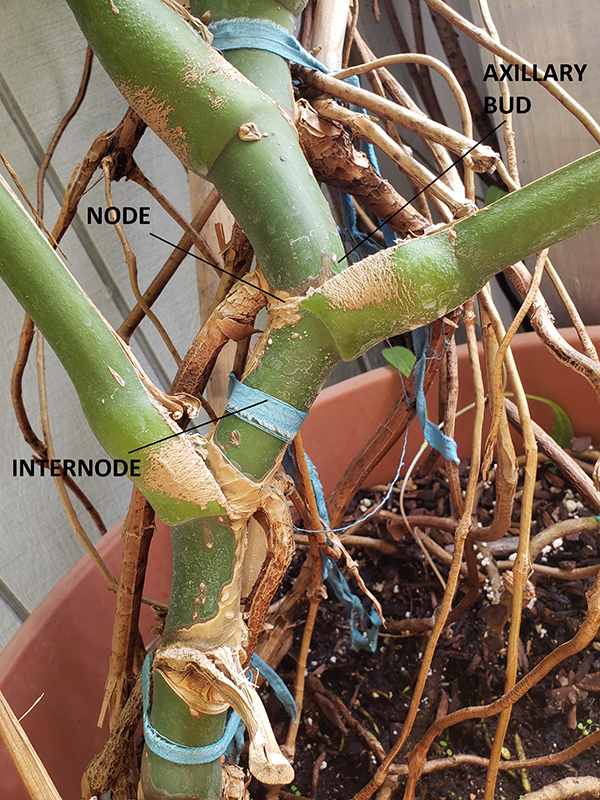
Stem cuttings are a popular method for propagating Monstera plants. To begin, select a healthy stem with at least one node. Use a clean, sharp knife or scissors to cut just below the node. Ensure the cutting is about 4-6 inches long.
Remove any leaves near the base of the cutting. This helps prevent rot. Place the cutting in water or directly into soil. If using water, ensure the node is submerged. Change the water every few days to keep it fresh.
In a few weeks, roots will begin to form. Once the roots are a few inches long, transfer the cutting to a pot with soil. Keep the soil moist, and place the pot in indirect sunlight.
Air Layering
Air layering is another effective technique for propagating Monstera plants. This method involves encouraging roots to grow on the plant before cutting it. Select a healthy stem and make a small cut just below a node.
Wrap moist sphagnum moss around the cut area. Secure it with plastic wrap to retain moisture. You can also use a twist tie to keep it in place. Check the moss regularly to ensure it stays moist.
In a few weeks, roots will begin to grow within the moss. Once the roots are visible, cut the stem below the new root ball. Plant the newly rooted stem in a pot with soil. Water it well, and place it in a spot with indirect light.
By using these propagation techniques, you can easily grow new Monstera plants. Enjoy watching your plant collection expand!
Care For New Plants
Once you have successfully propagated your Monstera plant, it’s crucial to provide proper care for the new plants. Caring for these young plants ensures they grow healthy and strong. Let’s explore the key aspects of caring for new Monstera plants.
Watering Requirements
New Monstera plants need consistent moisture. Water them thoroughly, ensuring the soil is evenly moist but not soggy. Check the top inch of soil; if it’s dry, it’s time to water. Overwatering can cause root rot, so always check soil moisture levels.
Light And Soil Needs
Monstera plants thrive in bright, indirect light. Place new plants near a window where they receive filtered sunlight. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
For soil, use a well-draining mix. A blend of peat moss, perlite, and orchid bark works well. This mix ensures good drainage and prevents waterlogging.
Common Issues
Monstera plants are popular for their unique, large leaves. But like all plants, they face common issues. These can affect their reproduction and overall health. Understanding these problems can help you maintain a thriving plant.
Pests And Diseases
Pests like spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs can harm Monstera plants. These pests suck the sap, leaving the plant weak. Regular checks can help spot these pests early. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to treat infestations.
Diseases such as root rot and leaf spot are also common. Overwatering often leads to root rot. Ensure the soil drains well. Leaf spot causes brown, yellow, or black spots on leaves. Remove affected leaves and keep the plant’s environment clean.
Growth Challenges
Monstera plants need the right conditions for healthy growth. Low light levels can cause slow growth and small leaves. Place your plant in bright, indirect light. Too much direct sunlight can scorch the leaves.
Improper humidity levels also pose a challenge. Monstera plants thrive in humid environments. Dry air can make the leaves brown and crispy. Use a humidifier to maintain ideal humidity.
Another challenge is improper soil. Monstera plants prefer well-draining soil. Using the wrong soil mix can lead to poor growth. A mix of potting soil, peat moss, and perlite works best.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Monstera Plants Reproduce?
Monstera plants reproduce via seeds or cuttings. For seeds, plant them in a moist, warm environment. For cuttings, use a stem with aerial roots and place it in water or soil until it roots.
Can Monstera Plants Reproduce In Water?
Yes, Monstera plants can reproduce in water. Place a stem cutting with aerial roots in water. Change the water regularly. Once roots form, transfer the cutting to soil.
How Long Do Monstera Cuttings Take To Root?
Monstera cuttings typically take 2 to 4 weeks to root. Ensure the cutting has at least one node. Provide it with indirect sunlight and keep it in a warm environment.
Do Monstera Plants Need Special Soil For Reproduction?
Monstera plants prefer well-draining soil for reproduction. Use a mix of potting soil, perlite, and orchid bark. This combination provides adequate aeration and moisture retention.
Conclusion
Monstera plants reproduce both sexually and asexually. Each method has its charm. Sexual reproduction involves flowers and seeds. Asexual reproduction uses cuttings and division. Both ways help Monstera thrive and multiply. Growing more plants can be rewarding. Understanding their reproduction methods aids in better care.
Happy growing!





